Big data and big data analytics have brought new concerns and opportunities in public auditing community.

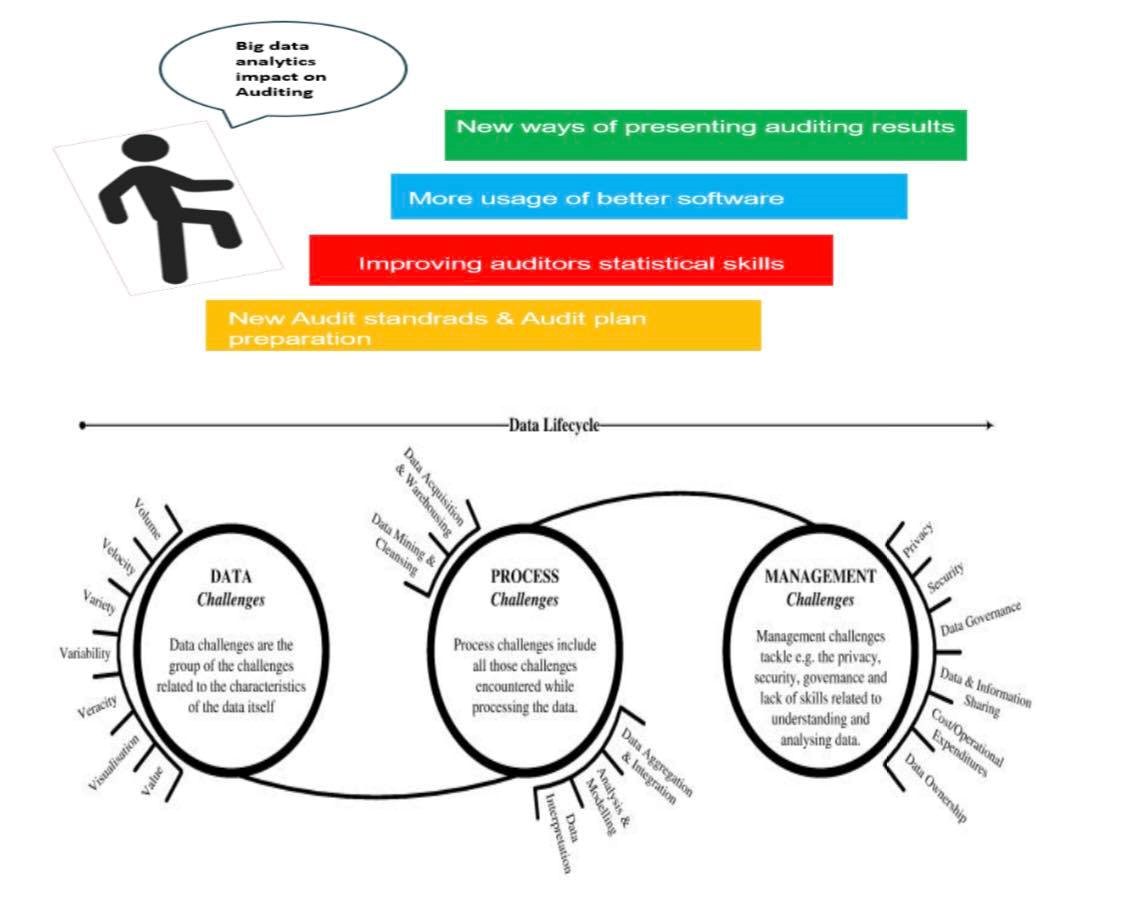
“Big data” is the term used to describe this massive portfolio of data that is growing exponentially. The general view is that big data will have a dramatic impact on enhancing productivity, profits and risk management. But big data in itself yields limited value until it has been processed and analyzed. On the other hand, IBM defined “Big data analytics” as “The use of advanced analytic techniques against very large, diverse data sets that include structured, semi-structured and unstructured data, from different sources, and in different sizes from terabytes to zettabytes”. New data analytics methods may change the way an audit is performed or conducted, which will lead to many changes in the auditing standards, the way auditing plans are prepared, how the auditing results are presented, improving auditor’s statistical skills and better usage of the software.
Big data auditing may lead to the enhancement of auditing performance (either auditors’ performance or auditing results), quality of auditing process and outcomes and improving governance performance promoting better decisionmaking, sustainable development of society and better public services provided.

Implementation of Big Data in Public Auditing:
In order to implement big data in public auditing, many stages need to be applied. First of all, data acquisition; identification of the most appropriate data to support compliance analysis procedure, multiple data sources must be considered – followed by gathering data from either structured or unstructured sources and appropriate platform independent technology is essential to provide rapid connectivity to a wide range of data types.
Second stage is the analysis procedure; various analysis types are performed. For example, examining entire populations of transaction data for a business process in order to determine if each transaction complies with a specific internal control or regulatory requirements or examining the same data in order to determine if there are indications of risks or compliance failures for which no control was established.
Third stage is dealing with massive data volume. In practice, when managing data volumes, consider that the data may be part of massive data elements that exist within the corporate and/or other databases. Thus, maintaining security and control over data used for audit and risk purposes.
Fourth stage is automation and continuous risk monitoring; Decisions need to be made once a library of data analytics and compliance tests have been established. Also, tests should be performed for critical exposures on a more frequent regular basis and scheduling continuous monitoring to determine responsibilities for responding to exceptions and addressing control and compliance risks.

Challenges and threats:
Auditors can face some issues and challenges during the application of the previous stages. These challenges can have a negative effect on their work, as an example the following: 1. Working on reliable data. 2. Data access, diversity of data. 3. Auditor experience vs. rapid change of technology. 4. IT architecture. 5. Lack of skills or experience. 6. Staff shortage. 7. Data capture. 8. Errors. 9. Costs. How to overcome the challenges:
There are many effective ways to overcome the previously mentioned issues and challenges. The organization should always seek to employ the best practices when it comes to IT in general and Data analytics in particular through the following: 1. Auditors’ continuous training in topics related to big data and big data analytics. 2. The implementation of international auditing standards and procedures when it comes to IT audit. (WGITA – IDI Handbook on IT audit for supreme audit institutions, Cobit and others). 3. Encouraging the auditors to focus on developing their technical skills and staying up-to-date on the latest technologies. 4. Information assurance. 5. Auditors should be able to find the appropriate balance between applying auditor judgment and relying on the results of the analytics. 6. Following regular audits which also help in improving the effectiveness of the audit. 7. The organization should always seek to hire qualified and skilled staff including auditors.
State of Audit Bureau of Kuwait and Big Data:
State of Audit Bureau of Kuwait has always aims primarily at the maintenance of public interest by safeguarding public funds and efficiently utilizing them for the aspects they have been allocated for communication with other authorities, to organize their financial and accounting transactions and devise the suitable solutions in order to reach the exemplary objective. State of Audit Bureau of Kuwait has always been supportive for his auditors, giving them the opportunity to explore and involve in the new technologies and approaches arise worldwide in order to enhance their performance and their auditing outcomes. State of Audit Bureau has taken several steps in prompting towards studying the feasibility of applying Big Data through:
- Joint the INTOSAI Working Group of Big Data. 2. Formed a delegation to participate in the Big Data Conference held in Washington DC April 2018. 3. Formed a delegation to participate in the Big Data Conference in Denmark April 2019. 4. An internal workshops and presentations had been performed to educate the auditors about Big Data.